Monitoring system
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
Resolution
-
A system called “Tide Database” (TDB) has been set up by the SHOM to store, process and give access to in situ sea level measurements and related metadata, such as vertical references, tide benchmarks, instruments, photos, etc..
-
Tidal observation reference network. All areas under national jurisdiction, in France and French overseas territories 1679 -
-

The national observation network for the blue mussel (MYTILOBS), set up in 2012, aims to monitor the growth and mortality of mussels produced for the market. The MYTILOBS is based on the experience of the regional network (REMOULA) which has been monitoring the growth of the blue mussel in the Charentais inlet since 2000. Monitoring mainly takes place the year following the year of capture: it thus integrates the main seasons of the biological life of the mussel, from winter maturation to spring growth, then to summer and fall fattening, the two periods when they are mainly sold. The choice of monitoring sites was decided in consultation between the Regional Environmental Resource Laboratories and the industry. For North Brittany, this is the site of Vivier-sur-Mer in (the sector of) the bay of Mont-Saint-Michel (mussel poles). Each breeding site is monitored every three months. Many parameters are measured including mussel size, weight and mortality. These data are examined taking into account environmental conditions such as temperature, salinity or the abundance and richness of the microalgae on which the shellfish feed. The Mytilobs national network is located in the main mussel-breeding regions of the Atlantic coast: Normandy, North Brittany, South Brittany, Pays de Loire and Poitou-Charentes. The sites of Agon (West Cotentin), Vivier (the bay of Mont Saint-Michel), Pont Mahe (Vilaine bay), Aiguillon (Breton inlet), Yves (Pertuis d’Antioche strait) representing, from north to south, mussel culture using poles. The Filiere site (Pertuis Breton - strait) represents mussels culture using ropes, in full water.
-
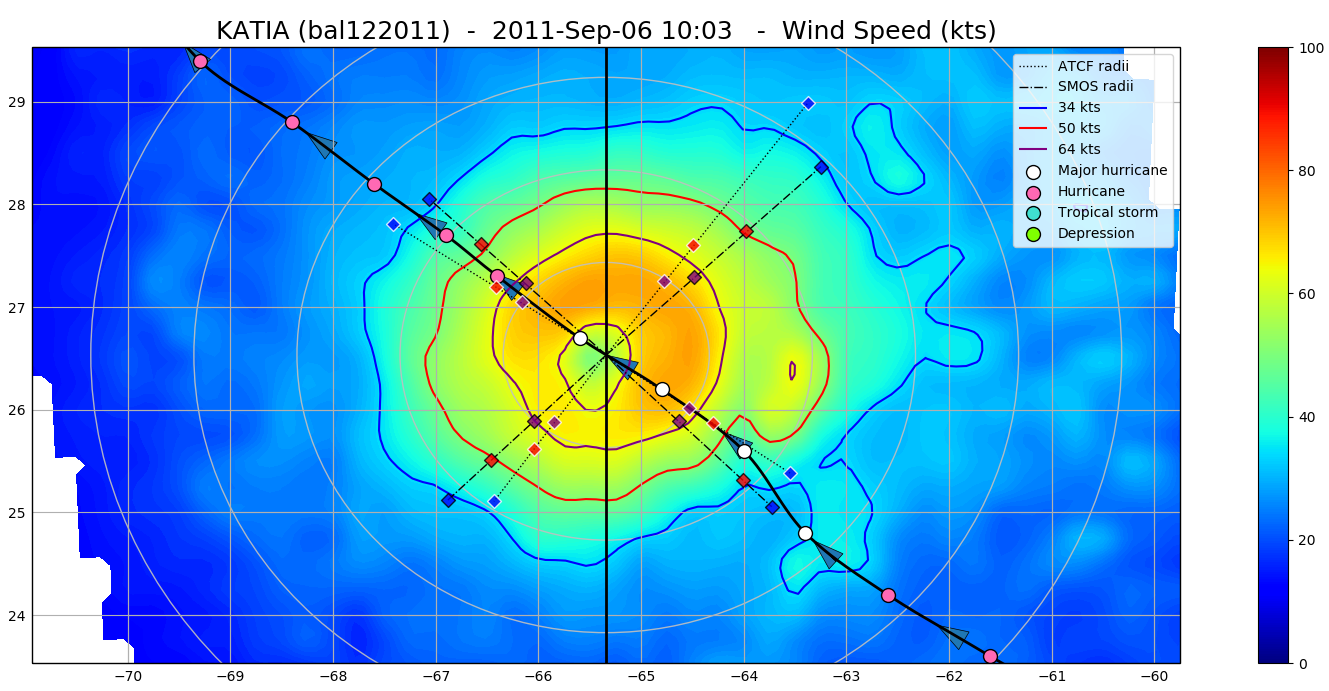
The SMOS WRF product is available in Near Real Time to support tropical cyclones (TC) forecasts. It is generated within 4 to 6 hours from sensing from the SMOS L2 swath wind speed products (SMOS L2WS NRT), in the so-called "Fix (F-deck)" format compatible with the US Navy's ATCF (Automated Tropical Cyclone Forecasting) System. The SMOS WRF "fixes" to the best-track forecasts contain : the SMOS 10-min maximum-sustained winds (in knots) and wind radii (in nautical miles) for the 34 kt (17 m/s), 50 kt (25 m/s) and 64 kt (33 m/s) winds per geographical storm quadrants, and for each SMOS pass intercepting a TC in all the active ocean basins. See the complete description the "SMOS Wind Data Service Product Description Document" ( http://www.smosstorm.org/Document-tools/SMOS-Wind-Data-Service-Documentation ).
-
-

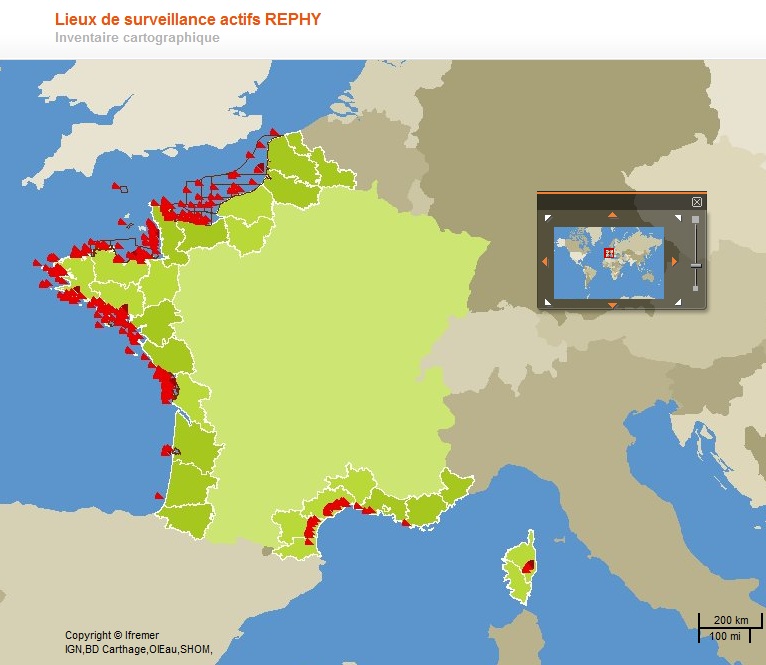
National network for monitoring the health status of shellfish populations in natural beds or in shellfish growing areas. It performs a regulatory role and a public service activity delegated by the Ministry of Agriculture and Fisheries through the DGAL (General Directorate for Food).
-
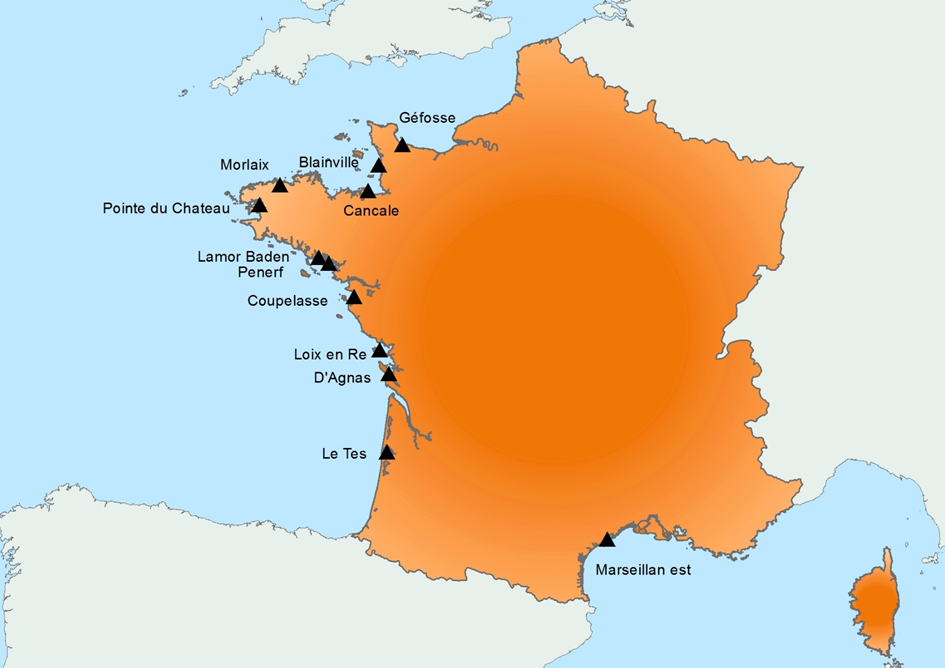
Created in 2015, it follows on from the RESCO launched in 2009, and REMORa launched in 1993. In 2015, the structure and operation of the former RESCO network was used to implement planned monitoring of oysters. More specifically, the sentinel batches used by the network, representing 3 age classes (6 months, 18 months of the previous year and 30 months of the previous year) are monitored regularly (frequency: bi-monthly or monthly). throughout the year at 12 national sites (corresponding to former RESCO sites). At each passage, counts are made to assess the mortality rate, and different types of laboratory diagnostic tests will be performed: - initially, the new spat batches (Ifremer Standardized Spats) will undergo specific PCR analyzes to search for potentially present infectious agents (OsHV-1 and Vibrio aestuarianus) but also non-specific analyzes (histology, classical bacteriology) for the possible detection of other pathogenis agents ; - for the detection of emerging diseases, the first dying batches detected for each age group, for each site, will undergo specific laboratory (OsHV-1 and Vibrio aestuarianus PCR) and non-specific (histology) diagnostic tests in order to detect as early as possible emerging diseases in these sentinel batches; - for the detection of exotic diseases, in the absence of a hierarchy of exotic diseases being available for oysters, it was decided to monitor the parasite Mikrocytos mackini because infection with this parasite is regulated at European level, on one of the RESCOII sites (Loix en Ré) previously identified as a site at risk with respect to the introduction of this parasite. In addition to these mortality follow-ups and the laboratory diagnoses, each site is equipped with a probe to allow it to gather environmental parameters (temperature, pressure, salinity) at high frequency. The various results are stored in the Quadrige² database, and are available for the various actors involved. The network is closely linked to a dedicated website which allows the dissemination of objectives, protocols and results, and which will be updated every month. In parallel, newsletters summarizing the results obtained are sent by e-mail every month to the State services.
-
-
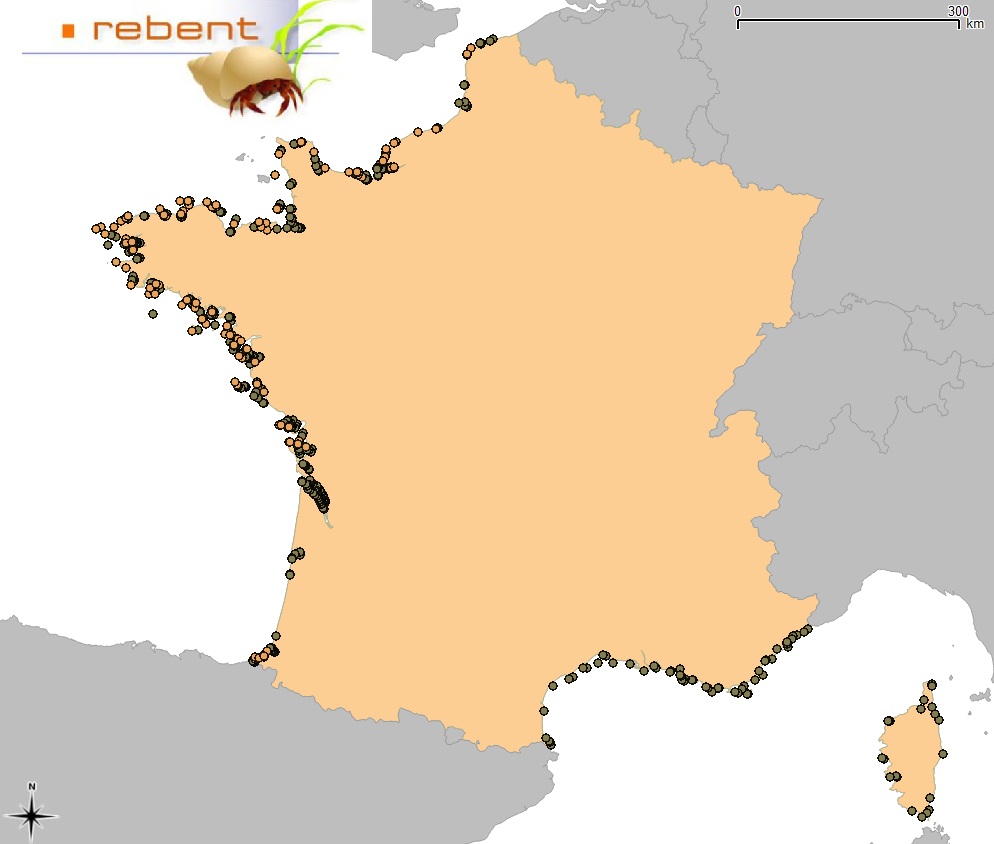
Since 2008, the Coastal Chemical Contamination Observation Network (ROCCH) has taken over from RNO (French National Observation Network for Quality in Marine Environments), which had existed since 1974. ROCCH aims to meet national, community and international obligations relating to monitoring chemicals in marine environments. It is therefore more of a control network than a heritage network as RNO once was. The backbone of ROCCH is to apply the European Water Framework Directive (WFD) and to meet the obligations set out in OSPAR Conventions and in Barcelona. As the WFD insisted on decentralization, ROCCH has gone from having just one project leader (the Ministry for the Environment) to having many decision-makers (water agencies, DIREN etc.). Chemical analyses are no longer conducted by IFREMER alone, but are attributed to other partners following calls for tender. ROCC also includes the monitoring of chemicals in shellfish production areas for the Food safety agency (DGAL) and the Ministry for Agriculture and Fisheries. Monitoring focuses on the three regulated metals: mercury, lead and cadmium in the given areas. Monitoring of these chemical contaminants is conducted in the three marine matrices: water, biota and sediment. Testing also includes imposex, the biological effect of tributyltin (TBT), as required by the OSPAR convention.
-
 Catalogue PIGMA
Catalogue PIGMA